AZS – atopic dermatitis.
During the first days of a child's life, the skin becomes dry rapidly due to the low activity of the sebaceous and sweat glands.. Therefore, it should be remembered to additionally lubricate it. Newborn skin care, and later, an infant requires constant care and protective measures. The skin is a natural immune barrier. It protects against harmful bacteria and allergens. All functions, that leather meets, unfold to the end 3 age. Children's skin is thinner than that of adults, and the natural water-fat coating is not so effective.
The first bath
Please note, that the water in which the baby is bathed, it can be of different quality and most often it dries the skin, even mature. Preparations used for care effectively lubricate and strengthen the skin's protective mechanisms, regenerate the lipid coat and stimulate the production of ceremonies necessary for the skin. It is best to do it in the evening, it should be a pleasant ritual to help your baby fall asleep. Bath lotion should be used for daily care.
Bath temperature should not exceed 36 degrees (close to the physiological temperature of the body). Too hot baths rinse out ceremides and lipids from the protective mantle of the skin, also in healthy people. Therefore, it is completely contraindicated in the case of dry and sensitive skin. The bath should last approx 5-10 minutes.
Putting the baby in the bathtub, hold them firmly with one hand and place them under the baby's back, the other, you can do other activities.
Do not use regular soaps and foaming bath lotions, because they reduce the effectiveness of emollient preparations and cause the leaching of lipids from the stratum corneum.
The area of skin folds in the groin, elbows and knees can be washed with a soft washcloth. Please note about washing your baby's hands and be careful, in order not to introduce the preparations into the child's eyes.
After slightly wetting the head should be washed with shampoo. Watering should be started from the head, remembering, so that the rinsed shampoo does not get into the eyes. Next comes the neck, torso and upper limbs, then the lower one.
Eye wash saline or boiled water from the outer corner to the inner corner, that is, from the temple to the nose.
The ears and nose do not need to be cleaned, unless there is a residual discharge in the nose. It should be extracted with a cotton swab or cotton bud.
Carefully take the toddler out of the bathtub and wrap it in a towel. Put the child on the table and wipe it dry, remembering, to make a towel gently apply to the body, a do not rub nim, as it wipes away the protective fatty layer of the skin! If your baby's navel gets wet while you are bathing inadvertently, you just need it dry thoroughly. The same goes for getting your ears wet, which also require thorough and gentle drying.
Within 3-5 minutes after bathing, rub the baby with a moisturizing preparation.
Treatment of atopic skin
WHAT IS ATOPIC Dermatitis (AZS)?
Atopic dermatitis is chronic, returning, inflammatory skin disorder, genetically determined. The course of the disease is very characteristic – periods of exacerbation alternate with periods of "calm symptoms" (remission). In recent years, the number of cases of atopic dermatitis and others, allergic diseases from the circle of atopy (such as hay fever, allergic conjunctivitis, bronchial asthma) rises sharply, which may be related to environmental pollution and increased sensitivity to allergens. Currently it is believed, that it is one of the most common childhood diseases (onset in approx 80% applies to children up to 5 age). Atopic dermatitis may go away on its own (especially if its course is mild), however, most patients throughout their lives are prone to excessive skin dryness and sensitivity.
What factors provoke exacerbations of the disease?
- Climate (high ambient temperature increases the amount of sweat, which irritates the skin),
- Environment pollution (chemical compounds weaken immunity and facilitate the penetration of allergens into the human body),
- Food allergens (milk products, haha, fish meat, nuts, chocolate, citrus),
- Airborne allergens (house dust mites, plant pollen, animal dander, allergens of bacterial and fungal origin),
- Mental factors (stress exacerbates itchy skin),
How to recognize your child's atopic dermatitis?
The main symptoms are:
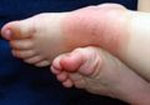
- dry skin
- skin changes (eczema, with the presence of lumps on the erythematous basis, erosion, often oozing),
- persistent, paroxysmal skin holidays (which may cause increased excitability of patients and disturbed sleep and appetite),
Location of changes:
The lesions have different locations in different age periods. It stands out in the course of AZS 3 phases:
I. The infancy period – do 2 age
The skin lesions mainly affect the face (the so-called. varnished cheeks) hairy scalp, less often the torso and buttocks.
II. The period of childhood (2-12 year of life)
The lesions are located within the elbow bends, knee, wrists, sometimes they affect the face and neck.
III. Adolescence and adulthood.
Any area of the body may be involved, but as a rule, lesions include the elbows and the knee bends, wrist area and face.
What to do if your child has AD?
Treatment of AD depends on the severity of the symptoms of the disease and is determined by the physician individually for each patient. It is often a complex and difficult process, always requiring the cooperation of the patient and his family. Both in the period of exacerbation and remission of the disease proper skin care is the basis of therapeutic procedures. The use of moisturizing and oiling products (the so-called. emollients) allows you to restore the lipid coat of the skin, thereby reducing water loss through the stratum corneum. The effect is to increase its elasticity and reduce the itching sensation by the patient. in addition, as a rule, treatment involves reducing the inflammation of the skin, soothing of irritation and, if possible, elimination of allergens and unfavorable environmental factors from the patient's environment.
What other treatments are used in AD??
- Topical anti-inflammatory preparations (steroids, macrolide derivatives),
- Antihistamines (reduce itching),
- Sedatives (ensure a good night's sleep),
- Antibiotics, antiviral drugs, or antifungal (recommended in case of skin superinfections),
- Light therapy (irradiation with lamps emitting ultraviolet radiation),
- Other general treatments, which can be used in severe cases, only in specialized dermatological centers,
- Psychotherapy.
All medications should be used strictly as prescribed by your doctor!!!
WHY IS PROPER SKIN CARE FOR YOUR BABY'S SKIN SO IMPORTANT?
The main symptom of AD is dry and itchy skin, Healthy skin produces a protective coat, which includes lipids, water and a natural moisturizing factor (NMF). Thanks to it, the skin does not lose moisture, it is soft and flexible. Patients with AD are deprived of this protective layer, therefore their skin is dry, rough, and its surface often cracks and peels off, which may favor the attachment of secondary bacterial infections.
The basis of proper care of atopic skin is the constant use of moisturizing and lubricating agents, and this regardless of the stage of the disease development, and avoiding factors that aggravate symptoms. Care preparations come in various forms: creams, ointments, bath lotions or oils. The best results are achieved through the use of comprehensive therapy – combination of an oiling bath with the use of creams that rebuild the lipid coat.
How to take care of your child's skin if he suffers from atopic dermatitis?
Regular baths with the addition of appropriate emollients play a huge role in the treatment of atopic skin. They allow the stratum corneum to be hydrated, removing allergens and irritants from its surface, Purification, increasing the absorption of topically applied medications as well, which is extremely important, have a relaxing effect. Great importance is attached to the use of emollients, as additives to the therapeutic bath. Thanks to these substances, we obtain lubrication of the skin, rebuilding its protective barrier and reducing the possibility of it losing water after bathing. The most suitable for atopic skin are preparations containing natural oils.
Thanks to the content of natural substances, the preparations help the skin to rebuild its protective barrier in a physiological and natural way, restore water balance and reduce moisture loss. Bath products, unlike the mineral substances remaining on the surface of the water, they completely disperse in the water bath.
How can you protect your child from ASZ?
Diet
Certain foods can aggravate the symptoms of the disease (most often they are: cow milk, chicken eggs, nuts, citrus fruits, fishes, chocolate, hot spices). Food hypersensitivity reactions are individual and are therefore sometimes difficult to establish, which products cause allergies. The diet is determined individually for each patient, by observing his reaction to particular foods. If your child suffers from AD, try to breastfeed as long as possible (minimum 3-6 months). If you are a nursing mother, eliminate potentially allergenic products from your diet.
Clothes
Avoid overheating the body and adjust the child's clothes to the ambient temperature. Only dress your child casual, airy, cotton clothes. Avoid wool, synthetic fabrics with uneven and rough texture and fur.
Jewelry and cosmetics
Items containing certain metals, e.g.: nickel, cobalt, chromium is often allergenic to AD patients, causing skin irritation at the point of contact with the skin. Be careful when using perfumed cosmetic products, because they often additionally irritate the skin.
Rooms
Avoid overheating the rooms, air them daily. Too high temperature promotes additional drying of the skin (the optimal temperature is around 20 degrees). Remove any items that are the source of allergens from the child's environment, e.g.: house dust mites, mold fungi, feathers and wool. Avoid smoking in the presence of sick people.
Sport
Avoid physical exertion, which leads to excessive overheating and intense sweating (sweat may irritate the skin). People with AD must pay attention to taking up activity and adapt it to the reaction of their own body.
Influence of climate and sunbathing
In most cases, climatic treatment in coastal or alpine regions brings significant improvements. The sun usually has a positive effect on the skin with AD. However, you should avoid intensive sunbathing and protect your skin from burns, using sunscreen creams.
Influence of stress and hygiene of life
Stress factors, unregulated and unhygienic lifestyle can often exacerbate the symptoms of the disease. A patient with atopic dermatitis should strictly adhere to the constant rhythm of meals, sleep, work, fun and relaxation.
The role of additional skin infections
The skin of AD patients is much more susceptible to infections, e.g.: fungal, bacterial and viral. They are usually caused by staphylococcus aureus bacteria and yeast-like fungi. Regular use of oiling and moisturizing products significantly minimizes the occurrence of such infections.