Alopecia
Hair loss is a natural phase of their development. We lose every day 50-100 hair. And this amount should not be completely worried. What else, when we notice a whole mass of hair on the bathtub after a bath or on a comb and the matter gains disturbing momentum. Why is this happening? Here are the most common causes of baldness:
- androgeny, that is, male sex hormones. And exactly their derivative called dihydrotestosterone (DHT). Sensitive hair follicles shrink and shrink instead of being strong, long hair, begin to produce thinner and more delicate, and finally only a delicate fluff. The tendency to be sensitive to this substance is hereditary. This type of androgenic alopecia affects approx 60 proc. white men above 50. age. It also happens in women.
- nervous system disorders, hormonal disorders, immune-mediated diseases. Cause, that the processes of cell division in the hair follicle slow down, producing thinner and weaker hair. In places, the name begins to thin out - alopecia areata. In some cases, hairless surfaces may merge, and even completely bald. The disease can appear at any age and resolve by itself, but relapses are possible.
- infectious diseases (typhoid, some forms of flu, tuberculosis, pneumonia, syphilis). Most likely, pathogenic bacteria or their toxins enter the hair follicle and disrupt its normal functioning. Prolapse may also be caused by a prolonged high fever.
Excessive hair loss (above 100 daily) is referred to as alopecia. It can affect anyone, both men and women. The most important thing is to react in time
and start the appropriate treatment. In many cases there is a chance to save your own hair.
It can also be a consequence: skin diseases, such as itching, seborrhea, dandruff, tinea, a strict slimming diet, cancer therapy, poisoning with drugs or cosmetics. Only a specialist can assess the condition of the hair and make an appropriate diagnosis.
Diseases and other causes of baldness
Celiac disease
It is caused by an abnormal immune response of the body to gluten in food. In this case, it is most advisable to go on a gluten-free diet. However, this is not always possible, and if gluten is not removed from the diet, people with celiac disease are at risk of losing their hair.
As an autoimmune disease, celiac disease carries the risk of developing other diseases of the immune system in the patient. Therefore, hair loss caused by another autoimmune disease such as alopecia areata has also been reported in people suffering from celiac disease..
A more common symptom in people suffering from celiac disease is a weakening of the hair fiber, which becomes thinner and overall hair loss. This is probably due to an inflammatory reaction in the gut caused by the presence of gluten, which inhibits the absorption of other nutrients necessary for proper hair development.
Similar symptoms (weakening of the hair) can be observed in people suffering from enteritis. Another cause of this condition may also be an abnormal hormonal balance in the body. In celiac disease, a strict gluten-free diet effectively prevents intestinal inflammation and, as a result, solves the problem of hair weakness.
Diffuse alopecia in women
The increased amount of hair loss and its general weakening all over the head is called diffuse alopecia. To know its cause, clinical trials should be performed. The medical history should cover, in particular, the diet taking into account the nutrients. It is also advisable to examine the thyroid gland, hemoglobin and the body's endocrine system. Stress can be another factor in overall hair loss, as well as too tight braiding the hair or tying it in a "ponytail".
Androgenetic alopecia in women
This genetic disorder is much more common in men, however, tens of thousands of women around the world are also losing their hair. What is the difference between baldness in men and women? Men more often go bald "to the point" or complain of "receding hairline". The problem of women is mostly androgenetic alopecia, which manifests itself all over the head. In women, it usually starts around 30. age (but it might as well be earlier). Thinning hair usually starts to be very noticeable around 40 years of age and may become even more apparent after the menopause. About half of women in their 50s will experience more or less severe hair loss and thinning.
Hair loss in women is usually general in nature (for example, in place, where was five now there are two hairs) not like a local man (bald spots on top of the head, for example). However, it also happens, that women have a receding hairline. As in men, the hair follicles close due to the action of hormones.
Pregnancy, stress, medication or an inadequate diet can cause hair thinning, but 70% women, who have experienced this phenomenon can attribute it to androgenetic alopecia, also known as female alopecia (ang. Female Pattern Baldness – FPB). A symptom of FPB is complete hair loss and special hair loss from the crown area or the hairline. In the hair follicles there, testosterone is converted by enzymes into much more active dihydrotestosterone (DHT). This powerful hormone inhibits the metabolism and formation of hair cells. Hair becomes weaker, and their bulbs shrink. Eventually they die off completely, which results in irreversible baldness.
Aging
With age, the action of hormones and the aging of the body causes the hair follicles to shrink. Normal is holding it back, the full process of its development. Bulbs gradually decrease, and the time it takes for the hair to grow shorter, which results in their serious weakening.
Hormonal changes
Hormonal changes are a common cause of hair loss in women. After having a baby or stopping the pill, many women experience hair weakness to varying degrees. This is usually a temporary phenomenon.
During pregnancy, hormonal changes in the body of a woman cause, that more hair follicles are in the growth phase. Two to three months after untreating, the hair returns to its normal life cycle and many go into a resting phase, which results in their increased loss. This can be seen on the brush or in the bathtub. It is usually a temporary condition and as the hormone levels return to pre-pregnancy levels, the symptoms will cease by themselves. However, if the increased hair loss continues for more than half a year after resolution, it may be a symptom of hereditary hair loss activated by pregnancy and childbirth and the associated hormonal changes.
Balding folliculitis
It is a type of scar alopecia, in which inflammation of the hair follicle is the most visible symptom. Bald spots appear slowly, and damage to the hair follicles is irreversible.
This disease has still not been clearly diagnosed. It is often accompanied by abnormal immune responses or impaired leukocyte function. Staphylococcus aureus may be the source of pustules and inflammation of the hair roots, however, in most cases the changes are caused by non-pathogenic bacteria.
This ailment occurs in both men and women, aged from 30 do 60 years (in women) or in mature males; very sporadic cases occur in childhood. Balding folliculitis often affects the scalp, but it can also appear elsewhere on the body.
Inflammation of the hair follicle
Bacteria are the main cause of folliculitis. The condition is characterized by ulceration around the nape of the neck, which may gradually cover the entire scalp. Pustules can contribute to scarring, initially small, which will harden over time, if not treated properly.
The most common disease affects the scalp, but it can also appear in other areas of hair on the body, such as intimate areas or armpits, and the skin around the ears.
Inflammation of the hair follicle is typical of young people, black men, but it can also occur in people of a different race and gender. Inflammation of the hair follicle can also be related to the irritation of the scalp with chemicals and bacteria.
Antibacterial creams and shampoos are used to treat this condition. These agents should be used regularly, until the infection is cured. Also, avoid shaving close to the skin while you are recovering.
Bellows lichen planus
It appears on hairy parts of the body and can result in permanent hair loss. It turns out, that almost 40% Alopecia areata cases are the result of an infection with follicular lichen planus. Even in adolescents the disease has been reported.
Hair loss as a result of this condition is uneventful - it affects small places on the scalp, on which the hair has thinned. They can get bigger over time, but the disease progresses very slowly and even after several years the effects may not be visible at first glance.
Bellows lichen planus is not a well-recognized condition that causes hair loss and can be distinguished from lupus, alopecia areata or any other scalp disease is difficult. However, most specialists recognize the subtle differences between these conditions.
Skin biopsy is a common diagnosis. This condition is manifested by an increased level of lymphocytes (immune cells) and the breakdown of immunoglobulins. Some specialists use a test called immunofluorescence to find where the antibodies are broken down in infected tissue. This method is also used to detect impetigo. Often, inflammation occurs around infected hair follicles.
The most popular treatment is the use of corticosteroids, however, their effectiveness is determined individually.
Lichen planus
The exact cause of the skin condition called lichen planus is unknown. Patients have a characteristic autoimmune reaction that occurs most often with other autoimmune disorders. Lichen planus can appear in people of any age, but most of the sick people are in the age range 30-60 years.
There are several types of lichen planus, the most common of these is papular lichen planus. It manifests as shiny pustules on the skin. With time and the disease develops, the pustules may turn pink, purple or brown spots. Hair often falls out in these places.
There are also others, rarer forms of lichen planus:
– Aactinic Lichen Planus – occurs only in warm countries, it appears on areas of the skin that are directly exposed to the sun
– Lichen Planus Spinulosis - Its symptoms vary, can cause hair loss and skin lesions in people exposed to chemicals, inter alia used in color photography. Also gold compounds, penicillin or quinine can contribute to the development of lichen planus in people with genetic conditions.
– Lichen planopilaris, also called lichen planus folicularis is the name given to every case of lichen planus, in which hair loss is combined with the appearance of pustules.
Lupus
Systemic lupus erythematosus (pour. Lupus Erythematosus Systemicus) is a rare disease with inflammation of many organs and systems, such as joints, heart, kidneys, skin, lungs, blood vessels and the brain. This disease affects 10 times more often women than men.
The cause of lupus is unknown, however, blood tests detect an autoimmune reaction, in which antibodies are produced against its own cells and tissues. In contrast to alopecia areata, where only the hair follicles are attacked, lupus' antibodies attack DNA and other substances in the nuclei of all cell types in our body.
In addition to the antibodies mentioned above (ang. ANA – antinuclear antibodies), antibodies against blood cells in the blood system can also develop.
Most patients develop a rash. A classic symptom is butterfly-shaped facial erythema, ignites on contact with sunlight. Similar rashes or bruises can also occur elsewhere. Another symptom may be hair loss, due to the general defense reaction of the organism.
Hair loss may stop, with changes in the stage of the disease, but in many cases, hair loss is irreversible due to scarring. Hair loss is associated with an increased amount of antibodies in the skin tissues. As with other autoimmune disorders, there may be a spontaneous remission of the disease.
Therapy usually involves the use of corticosteroids or other immunosuppressants. To hide the bald spots on the head, hair transplants are used.
Psoriasis
It is a fairly common skin disease, characterized by thickening and inflammation of the skin, often covered with silvery scales. Despite, that psoriasis does not itch, the diseased area of skin may be large enough and visible, that it will cause great psychological discomfort combined with a sense of shame and embarrassment.
Psoriasis often affects the scalp. In severe cases, there may be a hard "cap" extending beyond the hairline. There may also be minor ones, scattered or thick, concentrated "scales".
The exact cause of psoriasis is unknown, it is usually a family condition. Psoriasis affects approx 2% white people, much less often it occurs in people of other races. The first time it can manifest itself from the age of 10 do 30 years and come back later in life. Relapses may be the result of stress, skin injuries or other diseases.
Psoriasis is manifested by the overproduction of new skin cells (over ten times faster). As a result, living cells accumulate, creating characteristic thickenings covered with dead cells.
Skin mycosis
It is one of the most common diseases, faced by dermatologists. Tinea (pour. tinea capitis) is a disease that has been known for centuries, but relatively recently it was found, that the pathogen is fungi. With the development of microscopes, it has become possible to identify foreign bodies on the skin and hair of patients. They were recognized as fungal colonies.
Mechanism of skin mycosis development
The mycosis infection occurs most often through the penetration of fungi into the body through small wounds or scratches. After breaking through the outer layer of the skin, they begin to multiply and expand in a circular manner, creating circles similar to these, which are formed after throwing a stone into the water. Mushrooms like to locate around the hair follicles, getting there through the hair fiber. This weakens the hair, which become brittle and breakable. The disease takes many forms, depending on the pathogen, type of hair and individual immune response. Some types of mycosis can manifest as visible inflammation that sometimes leaves scars. Some infections spread over the entire scalp very quickly, others develop slowly, causing slight hair loss.
Typically, an infection develops, occupying an area of about four centimeters radius. In most cases, the infection clears after approx 7 months. For some people, however, it may take much longer. The main symptoms of ringworm are scaly skin, sometimes inflammation is visible. This may look a bit like dandruff. Hair loss may occur along with skin lesions. Infected hair is brittle and brittle. Patients may develop small bald spots.
Diagnosis
In the past, other conditions that resulted in "plaque" hair loss were often mistaken for dermatophytosis. Even today, some dermatologists may confuse ringworm with alopecia areata. However, techniques are available to identify the presence of fungi. The simplest method is to use a Wood lamp. It is a small ultraviolet light lamp with a limited wavelength spectrum. Hair and skin infected with mycosis glow fluorescent green in the light of this lamp. However, this method does not provide 100% certainty. To confirm the test result with Wood's lamp, dermatologists usually take a tissue sample and grow it.
Ringworm spreads easily. Mainly through physical contact with an infected person, but also through hairbrushes, hats or chairs, because infected hair also spreads the disease. There are frequent epidemics in schools, where even 50% children may catch ringworm.
Treatment of mycosis
Treatments vary, depending on the stage, the type and appearance of the infection. Some of them will disappear spontaneously, without treatment. The most common, however, is an antibiotic called Griseofulvin, which is very effective in the fight against mycosis of the scalp. Griseofulvin gradually builds up in the skin and hair, especially by binding to keratin, the main component of hair and nails. Most people tolerate this drug very well. For some, however, Griseofulvin causes abdominal pain side effects, headache and feeling tired.
Scarring alopecia
If you have inflamed the hair follicle due to an infection, this can lead to the development of scar alopecia. This is a fairly easy case to diagnose, because rough "patches" will appear on the scalp, formed from blood vessels and connective tissue. Scarring alopecia has various causes and symptoms, here are some of them:
Lupus
Lupus is a disease of the connective tissue, as a result of which you may lose your hair on the head. In this case, there will be lesions around the scaly pustules within a radius of approx. 5-10 mm from the hair follicle. The skin may also become smooth and scarred. Lupus is a medical condition characterized by sensitivity to sunlight, so it should be avoided.
Hair follicle degeneration
It is a type of scar alopecia, which manifests itself first in diffuse hair loss. Sick area usually (but not always) it grows radially from the top of the head. Skin biopsies showed, that the condition is characterized by inflammation of the hair follicles.
FDS (ang. Follicular Degeneration Syndrome) was first diagnosed with an African American woman, overuse of hair straightener and oily pomades. It was judged, that the pomades applied to the hair and heated by the straightener have warmed up and liquefied, then penetrating through the hair fibers to the root, irritating it and causing inflammation of the hair follicle. Today, however, it is known, that straightening your hair can only exacerbate this condition, and the disease also occurs in people who do not use this type of treatment.
Typically, treatment focuses on combating inflammation in the hair follicle with corticosteroids, which, however, do not provide 100% certainty of a cure.
Scleroderma
Scleroderma is an autoimmune condition. In the early stages, inflammatory cells can be seen in the layer of the dermis. Scleroderma is manifested by gradual hardening and tightening of the skin due to the overproduction of collagen. Excess collagen stops the normal functioning of the hair follicle in a way, which can be described as "choking". Despite the large amount of collagen and infected hair follicles, the condition is not characterized by scarring.
Increased collagen production results in the appearance of skin spots and gradual hair loss. Hair loss is sometimes the first symptom of scleroderma, preceded by their graying. Sometimes hair falls out in a linear fashion on the scalp, which looks like a scar from a saber cut (hence the French is called linear scleroderma – saber-stroke). En coup de saber treatment usually requires surgical intervention to remove the affected skin.
Eczema
Eczema (pour. Seborrhoeic dermatitis) is inflammation, manifested as big, reddened area covered with yellow scales, which may include the scalp. Sometimes it also spreads to the forehead, the area around the ears and the nape of the neck. Scars and redness also appear on the chin, ears, nose, chest and groin.
Eczema occurs, when the sebum is infected with yeast. This is manifested by itching, peeling of the skin and redness.
The exact cause of eczema is unknown, is suspected, that the disease is genetically determined.
The severity of the disease is an individual matter. Factors such as stress or a poor diet can exacerbate the disease.
Treatment of eczema is symptomatic. Inflammation and skin changes are fought. Daily use of shampoos is very important. The time to wash the scalp does not play an important role here, what frequency of treatments.
Telogen effluvium
Telogen hair loss is caused by sudden stress. Such a strong emotional response may result in hair follicle development stopping and premature transition to the telogen phase (sleep). The hair then remains in the resting phase for approx 3 months, then they fall out.
In most cases, hair loss is temporary and new hair grows back after a short time. However, sometimes the disease is prolonged, until its cause ceases. Telogen hair loss affects women more than men, as they are more prone to stress, also the one related to pregnancy and childbirth.
Here are some factors, which can cause temporary hair loss:
• Termination of pregnancy
• Surgical procedures
• Use of birth control pills
• Taking dietary measures
• Severe emotional stress
Hair loss after the baby is born
Often, women lose their hair for approx 3 months. This process is caused by sudden hormonal changes. Statistics say, that from 20% do 45% mothers lose their hair after birth. Fortunately, most of the time everything returns to normal within a short time 9 do 12 months after termination.
Lots of women notice, that their hair is thicker and healthier during pregnancy, which is associated with increased levels of estrogen and progesterone in the blood. These hormones do, that more hair follicles than usual are entering the growth phase. After the baby is born, the change in hormone levels again puts the hair into a dormant state. As a result, after 3 months fall out.
Hair loss due to miscarriage
Just like it happens after giving birth, sudden hair loss can also be the result of a miscarriage. It is related to hormonal changes - hair goes to sleep and falls out after about three months.
Hair loss due to the use of birth control pills
Contraceptive pills affect the level of hormones in the body and, hence, hair growth. In some cases, hair thinning may be due to the male hormones found in some contraceptives. This type of hair loss can resemble androgenetic alopecia. However, stopping the pill can result in hair loss similar to that after having a baby due to hormonal changes..
Hair loss due to gastric surgery
Surgical and gastric procedures are used in the case of serious overweight. Such an operation is very stressful for the body and the immune system. Sudden weight loss due to the reduction of the stomach also results in a reduction in nutrient stores, which is reflected on the skin and hair. The hair becomes thinner, and their possible loss is temporary and the situation returns to normal after weight stabilization (from 18 do 24 months). However, people after 40. years of age may take into account irreversible hair weakening.
Surgery
The shock of major surgery can result in hair loss. Telogen effluvium almost always occurs after hair follicle transplantation. The bellows will therefore fall out within 3 months, after which new hair will grow out of the transplanted cells.
Hair loss caused by medication
You know, that certain medications cause hair loss. Of course, not all patients who take them will go bald, but some agents cause more frequent alopecia than others.
If you suspect, that drugs, which you take contribute to increased hair loss, consult your doctor or pharmacist.
Hair loss caused by stress
Some people experience telogen effluvium or sudden hair loss after traumatic events, such as the death of a family member or loved one, accident, divorce, rape and others. These events can cause the hair follicle to go to sleep too early, what after 3 months results in their increased loss.
The above cases are usually temporary and the hair will grow back soon.
Trichotillomania
Trichotillomania is obsessed with hair. People suffering from it pull and tear their hair out, which results in the appearance of bald "patches". The condition usually begins with pulling out different hairs, e.g.. coarser to the touch or curlier. Once the bald area has formed, pulling out more hair becomes more and more alluring for the patient.
Sometimes hair pulling is more general and resembles diffuse alopecia. Although this form of hair loss leaves no scarring or inflammation, this long-lasting hair-pulling can lead to irreversible damage to the hair follicles.
Trichotillomania affects 2-3% people, who have experienced hair loss. About 70% of them are stripped of the hair on the head, 50% on the eyebrows or eyelashes, 30% pubic hair, 20% it focuses on all body hair 10% people with facial hair.
It happens, that the plucked hair is eaten or chewed. Eating hair is known as trichophagy, and can result in a puff of hair in the stomach (called bezoars). About 40% the sick chews their hair, while 10% the sick eats them. This can irritate the stomach and lead to digestive problems and stomach ulcers.
This disease can affect both adults and children, however, almost all affected adult patients are female.
Many people with trichotillomania are unaware of it, what are they doing. Psychiatrists considered hair-pulling as a mental disorder, the most effective treatment is appropriate therapy at the clinic.
Mechanical hair loss
A mechanical cause of hair loss in an adult may be a hairstyle that causes excessive tension in the hair (“a pony tail”, really). In these cases it is recommended to change the hairstyle. If it is done in good time, the hair will grow back completely. Too late intervention will result in permanent alopecia due to the disappearance of the follicles.
For toxic reasons
Hair loss due to toxic causes occurs mainly as a result of poisoning, e.g.. such, arsenic, mercury. In the case of thallium poisoning, there are characteristic changes in the hair structure visible on microscopic examination. Alopecia appears after approx. 2 weeks after ingesting the poison, hair loss is almost complete, and regrowth occurs after approx. 6-8 weeks. In case of poisoning, the treatment of the patient is primarily the administration of the antidote and
Baldness does not equal baldness?
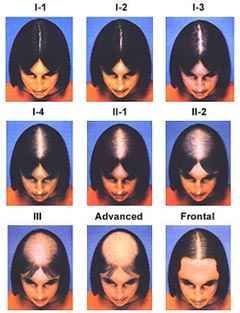
To be able to precisely define the stage of baldness and predict its progress, special scales have been created. The two primary ones are scale Norwood-Hamilton (in short Nw.) depicting baldness in men and the Ludwig scale - illustrating this process in women. Both relate to androgenetic alopecia, which is similar for most people.
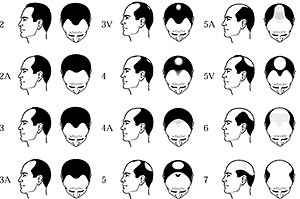
Androgenetic alopecia in men does not deprive them of their hair overnight. To proces, which lasts for years. It starts with characteristic bends above the forehead, gradually worsening with age. Lack of therapy results in further progress in rubbing the hair, this time on top of the head. In the final stage, the so-called. chaplet, that is, hair on the sides and on the back of the head. Discovered, that they are immune to the hormone that causes hair loss, which contributed to advances in transplantation.
What is the treatment at each stage of hair loss? Generally it is believed, that the first group of Nw. 2-3And this is just the beginning of baldness and starting therapy at this stage gives the best results. Available medications can stop the disease and lead to hair regrowth. Another group of Nw. 3V-5 is already an intermediate and advanced stage of baldness. Drug therapy can stop further hair loss, but you hardly ever get your lush hair back. And finally, the last group of Nw. 5A-7 are patients with very advanced baldness, for whom the only hope for improving their appearance is often a hair transplant.
Female androgenetic alopecia differs from male pattern baldness in that, that the hair is gradually thinning all over the head. At the same time, less often than in men, it reaches a very advanced stage, that is, almost or completely baldness.
Recent studies confirm, that baldness is not merely an aesthetic problem, but it has a huge impact on quality of life. Most people who lose their hair develop mental health problems, kinks, depression. It is hardly surprising, considering the fact how huge a role, not only the aesthetic one, has played hair in all communities throughout the ages.
Alopecia and sexuality
Probably none of us can imagine ourselves without hair (before losing them). Therefore, it is often associated with a reduction in self-esteem. It is hardest for young people to bear, who may even therefore experience sexual dysfunction related to a fear of rejection by the opposite sex. The best solution is to see a dermatologist immediately, remembering, that the sooner we act, the more effective the therapy will be.
Latest discoveries
The guilty genes?
Russian and American scientists working together under the leadership of Anastasia Kazanceeva discovered Gen., whose mutation may contribute to alopecia. An article on this subject was published by the weekly "Science". Tested 350 thousand. people suffering from hereditary hair growth disorder and premature alopecia. Although they were healthy people, their hair was very sparse and thin, and in some they began to fall out as early as childhood. They found mutations in the LIPH gene active in the hair follicles. It is responsible for the work of an enzyme called lipase H., which, in turn, controls the production of lysophosphatidic acid. Its deficiency probably inhibits cell division, from which hair is made. Scientists believe, that this is the beginning of a new era in hair loss research.
If you notice a characteristic rubbing of the hair on the temples and on the top of the head, you can blame it… your ancestors, and you inherited two genes from them, that were discovered by scientists. They believe, that this is the beginning of the invention of the cure for hair loss. Genetic tests were carried out on representatives of the white race, because it is them who are most affected by the problem of male androgenetic alopecia. However, scientists believe, that it is likely that the same genetic factors also appear in males of other races. The results of this international study are described in Nature Genetics. The "culprits" of androgenetic alopecia were found on the chromosome 20. The results of the research were confirmed on another 1,650 group of men, to confirm the results. Based on them, it was estimated, that the record of this ailment carries in its genetic code approx 14% men. By the way, the theory was refuted, that we inherit a predisposition to alopecia along with the X chromosome, that is, we get it from the mother. Research led by Dr. Richards dispels this belief. Dr. Richards does not give a date when the antidote for hair loss was invented. Argues, that there are many years of research and experiment ahead of him. Finding the cause is over
however, a great success, which points in the right direction.
You smoke? You will lose your hair faster!
As it turns out, smoking and environmental pollution can significantly accelerate hair loss. English scientists from Queen Mary University of London came to such conclusions. In laboratory conditions, they tested samples of hair follicles taken from balding men. The results of the experiment showed, that the toxic substances found in cigarettes, as well as those circulating in contaminated air, have an adverse effect on hair growth – production of proteins, they are built of is largely blocked.
Obviously, people with a hereditary tendency towards this tendency are more likely to lose hair faster. The so-called. androgenetic alopecia affects both men, as well as women. In men, the problem with baldness usually appears before 30 year of life, in menopausal women.
So was it quitting smoking and moving to an ecologically clean area?, you can keep your hair longer? The scientists led by Professor Mike Philpott are convinced, yes. They want to continue their research, to prove the effect of nicotine even more clearly
and other poisonous substances to weaken the hair.
Hypnosis will stop hair loss?
Mental factors play a significant role in the development of alopecia areata, or alopecia areata, e.g.. stress. Dr. Ria Willemsen of the Free University of Brussels believes, that hypnosis treatment can significantly improve the patient's well-being, and thus stop baldness. He was subjected to such therapy 21 people, have been losing their hair to say the least 3 months. Each of them had taken medications before, but they did not bring any improvement. When treatment is combined with hypnosis sessions, during which patients had to imagine, that their hair grows back, u 9 of them… it has really grown completely. In the case of the rest, the effects were less spectacular, a u 5 relapse of the disease was noticed. However, it is not known whether hypnosis or other therapies were performed in the "hairy" lucky ones.
source: Yahoo!
Hair anew
So far it has been tried, that nothing will help damaged hair follicles. It turns out, that the hair can be recovered. Such conclusions were reached by scientists from the University of Pennsylvania School of Medicine. Conducting research on mice, discovered mechanisms, which lead to the regrowth of hair follicles in rodents. They proved, that stem cells in the epidermis are responsible for this! This is a great hope for everyone, which currently known therapies are unable to help. Technologies based on this discovery have already been patented by the University of Pennsylvania School of Medicine.
Coffee strengthens your hair
This should not be taken literally. If we wanted to get the right concentration of caffeine that is beneficial for the hair follicles, we would have to drink until 60 cups of coffee a day! According to Dr. Tobias Fischer of the University of Jena, the caffeine in coffee beans blocks the substance, which damages hair follicles and stimulates new hair growth. However, baldness cannot be stopped, drinking coffee. Such a high concentration of caffeine could endanger your health, and even life. The discovery of scientists, who continue their research, however, was used by the German cosmetics company Alpecin, which created a caffeine-based product to lubricate the scalp.
Hope in stem cells
Perhaps the problem of baldness will disappear soon. Scientists are working hard to discover the mechanisms that regenerate the body. The study of primary stem cells is the key to success.
When a salamander loses its tail, her new one grows up. Similar regenerative abilities were discovered by accident in laboratory mice. Observed, that in rodents with deep wounds, the hair follicle is restored, from which new hair grows. This phenomenon is very similar to the processes, which occur at the beginning of the formation of a new life in the fetal period of each organism. Scientists have managed to speed up this process. Nature magazine quotes Dr. George Cotsarelis, professor of dermatology at the University of Pennsylvania School of Medicine, who thinks, that we must forget about it, that baldness is irreversible. The experience with mice proves emphatically, that hair follicles can be recreated and soon it will also be possible in humans.
How the experiment was carried out? A special preparation was applied to the skin of the mice, stimulating epidermal cells to transform into normally functioning hair follicles. The only drawback of the hair they produce is the lack of dye - they were white. The hair of the mice from the experiment was covered with patches. Would it be the same for humans? Or would all our white hair grow back?? It is not known yet. The patent for the preparation stimulating hair regrowth was purchased by Follica Inc. However, before it starts producing it, at least it will pass 5 years.
Meanwhile, Dr. Cotsarelis is conducting further research, so that not only the hair follicles are present in the reconstructed skin, but also the sweat glands,
which ensure the proper functioning of the skin.
Androgenetic alopecia is not just a male problem. To a greater or lesser extent it touches up 50% women in different periods of life. Mostly the disease shows up:
- After menopause, when the amount of female hormones estrogen decreases, and testosterone levels increase in parallel
- In adolescence, often following a slimming diet that strains the body
- Right after pregnancy, enhanced by the stress and iron deficiency associated with it.
When less and less hair
Hair loss in women begins at the top of the head. Hair is thinning, without covering the skin sufficiently.
As a rule, it is a very slow and gradual process. However, there may be a sudden worsening of the disease caused by other conditions, operations, strong stress or sudden weight loss. In menopausal women, hair loss of the temples similar to this also occurs occasionally, which characterizes men. However, there is rarely a case of complete baldness. The severity of female baldness is determined, using Ludwig's scale, which divides them into three basic phases: light, medium and serious.
Testosterone in the female edition
Female androgenetic alopecia may be associated with overproduction of male hormones or an increased sensitivity to them of the hair follicles. Then the testosterone level does not have to be too high.
Therefore, good results of hormonal tests do not exclude the diagnosis of androgenetic alopecia - as shown by studies in 50% in balding women the hormones are perfectly fine.
The worry of young mothers
Hair loss after childbirth is a completely normal process. Hormonal changes during pregnancy cause, that more hair follicles are in the growth phase and therefore the hair becomes more luxuriant during this period, there may be even several thousand more. After the baby is born, these follicles go into a dormant state, and the hair begins to decline. After a year, everything returns to normal.
A new, surprisingly simple method of testing the amount of hair loss has been developed – you just have to count them after one minute of combing. The results of the work of US dermatologists are published in the latest issue of the journal “Archives of Dermatology”.
“Until now, there has been no widely accepted standard method for determining the amount of hair we lose each day” – the authors of the work explain. Received, that we have around 100 hair, because with 1000000, which we wear on the head around 10 percent is resting. Generally speaking, this theory is plausible, however, it has not been scientifically proven and does not contain any information on the effects of age and gender on the hair loss process in healthy people.
Doctor Carina Wasko, at Baylor College of Medicine in Houston and their team studied hair loss in a group 60 healthy men in between 20, a 60 year of life, without any signs of baldness. Identical combs were distributed to all project participants and asked to wash their heads with the same shampoo for three consecutive mornings. On the fourth day, the gentlemen were asked to comb their hair by 60 seconds over a towel or pillow that is contrasting to the color of their hair, and then to count the hairs, that fell out.
The combing and counting experiment was repeated on three consecutive days, just before washing your hair, and the volunteers repeated the experiment for more 6 months.
The results of the study showed, that in between 20, a 40 years of age, men lose daily from 0 do 78 hair, medium 10,2 hair in 60 second test. Gentlemen in between 41, a 60 lose their lives daily from 0 do 43 hair, medium 10,3 hair in the test.
“Summarizing our experience can be said, that 60 The second test is a simple and effective method to determine the condition of your hair during morning brushing” – the authors of the work conclude. “Small differences between the individual participants of the study indicate the reliability of the test and the ease of its execution by patients” – scientists add.
Now, with a new simple method, it will be possible to test hair loss in women and in various disease states. WHEN